Liquidity Book Primer
What is the Liquidity Book AMM?
Dive into the innovative world of decentralized finance with Merchant Moe, where cutting-edge technology and efficiency converge to revolutionize trading experiences. At the forefront of this evolution on the Merchant Moe platform is the Liquidity Book protocol, an integral component of the Merchant Moe ecosystem.
Think of Liquidity Book as the powerhouse under the hood of a car. It operates beneath the surface of the Merchant Moe platform, linking liquidity and trades to enable the many transactions occurring on the platform. Unlike traditional centralized exchanges, Liquidity Book doesn't depend on order books. It leverages a Pool of funds, contributed by users, to conduct trades directly on the blockchain. This translates to faster, more streamlined transactions and a decentralized trading experience that puts you in the driver's seat.
At Merchant Moe, Liquidity Book emerges as a revolutionary tool. It's engineered not only to accelerate and streamline token trading but also to amplify profitability for liquidity providers (the fuel powering every trade). With its unique approach to managing and optimizing liquidity, it paves the way for everyone to benefit from the booming DeFi market.
Whether you're an experienced trader or just getting started, Liquidity Book provides an accessible and rewarding entry point into the realm of decentralized finance. Let’s embark on a journey to discover how it's redefining standards in the DeFi space.
To delve into the comprehensive details of Liquidity Book, check out the linked whitepaper.
Liquidity Book Key Features
Liquidity Book is more than a mere trading platform; it's a hub of innovative features designed to benefit both traders and liquidity providers. Let's explore some of these key features:
Concentrated Liquidity: Unlike conventional AMMs that disperse liquidity over an extensive price range, Liquidity Book enables liquidity providers to focus their funds within specified price brackets. This enhances the capital's efficiency, facilitating larger trades with minimal price slippage. For traders, it results in more stable and predictable pricing, while liquidity providers can capitalize on increased fee income opportunities.
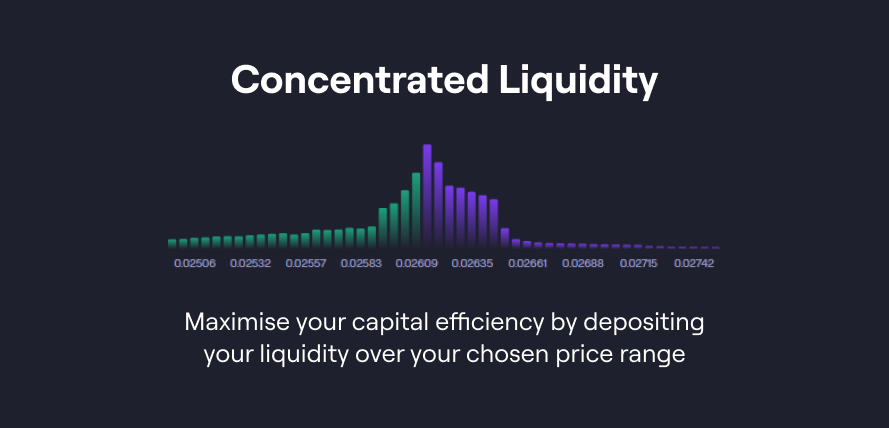
Surge Pricing: Liquidity Book introduces a dynamic surge pricing mechanism in reaction to market volatility. This system adjusts trading fees in real-time, reflecting current market dynamics. While traders might experience a minor increase in trading costs during turbulent periods, liquidity providers benefit from augmented fee earnings during peak market activity, offsetting risks like impermanent loss.

Bins Architecture: Liquidity Book incorporates a novel 'bins' system, essentially segmented pools of liquidity at specific price points. Each bin reserves liquidity for a designated price point, and collectively, they form a unified Liquidity Pool. This innovative structure minimizes price impacts during trades, offering traders optimal price execution. For liquidity providers, the bins arrangement enables a more tactical allocation of funds, optimizing their earning potential based on market trends.

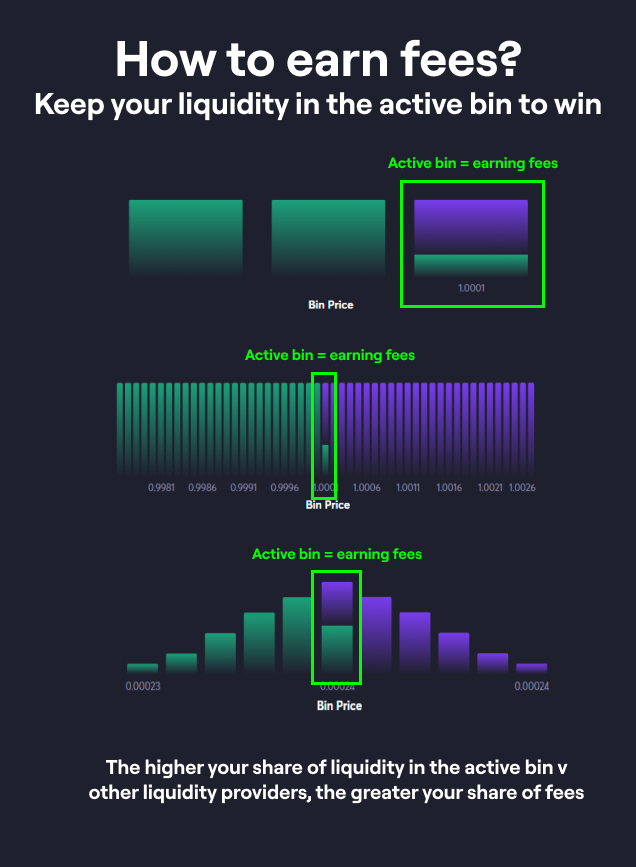
What is the active bin and how can I earn fees?
The active bin represents the current market price of assets within a Liquidity Pool. Only the active bin consists of both tokens and only the active bin earns trading fees. For liquidity providers, maintaining liquidity within this active bin is crucial to continuously accrue trading fees. As the market price shifts and a new bin becomes active, the previously active bin ceases to collect fees, emphasizing the importance of strategic liquidity placement.
You only earn trading fees from Liquidity that is in the active bin.
What is slippage and how does Liquidity Book solve it?
On traditional AMMs, asset prices depends entirely on a pool's composition, fluctuating with every trade. Buyers nudge prices up, sellers bring them down, leading to 'slippage' on every trade. This is when the final trade price deviates from the initial quote. Thanks to it's innovative bin architecture, Liquidity Book allows for swaps with zero slippage, meaning that advertised prices match the rates at which the trades were actually executed. This ensures that the price you see is the price you pay, allowing for precise and efficient trading.
Zero slippage ensures accurate prices are quoted when executing a swap.
How does re-balancing work on the Liquidity Book?
For liquidity providers to maintain their fee earnings, it's essential to rebalance their liquidity if it moves out of range of the active bin. This rebalancing involves removing tokens from inactive bins and redeploying them to ones closer to current price ranges. Liquidity Book simplifies this process with its fungible token receipts, enabling providers to adjust their positions with low gas costs and in a single transaction.
Re-balance to ensure you keep your liquidity in range to earn trading fees.
What are some considerations when re-balancing?
Costs: Rebalancing involves paying for gas and buying and selling assets, which can incur trading fees. It can be helpful to consider these costs when deciding how frequently to rebalance.
Market conditions: Rebalancing on Liquidity Book should take into account market conditions, as different market conditions may require different rebalancing strategies. For example, in a volatile market, an LP may need to rebalance more frequently.
Re-balancing will cost gas and any swap fees you from trading you execute.
What are the risks involved?
When liquidity is densely concentrated within a narrow price range, it heightens the risk of 'impermanent loss.' This occurs as assets are more closely bunched together, which could result in a permanent loss if not carefully monitored and managed. It's important to keep an eye on this and actively manage it to reduce risk.
Active Liquidity provisioning is complex and requires careful management.
Compare IL from traditional AMMs to concentrated AMMs
Engaging as a liquidity provider in an automated market maker (AMM) inherently involves the risk of impermanent loss (IL). This term refers to the decrease in the value of your pooled assets compared to if they were just held in your wallet. IL arises when the relative market prices of these assets shift away from their initial deposit levels. Concentrated liquidity amplifies this risk, as funds are more densely allocated within a limited price span. However, this approach can yield higher trading fees, offering liquidity providers (LPs) a trade-off between increased risk and the opportunity for greater rewardsThis is because the liquidity is more tightly packed into a narrower range.
Impermanent Loss can be mitigated by ensuring you kept your position balanced.